1 Cooling water treatment technology
The problems of corrosion, and encountered in circulating water systems can be solved by water treatment technology. Only the cooling water treatment technology can be used, and the technical and economic benefits after the cooling water circulation can be fully exerted. The so-called cooling water treatment technology refers to the correct matching of the water treatment formula, the corrosion inhibitor, the scale inhibitor, the dispersant and the biocide to the water quality, equipment material and working conditions of the circulating water system. Process control conditions, corresponding cleaning, pre-filming schemes, etc. are proposed. This whole process is called cooling water treatment technology. Among them, a corrosion inhibitor, a scale inhibitor, a dispersant and the like are formulated to determine suitable process control conditions, and the basic treatment and normal operation of the circulating cooling water are performed, which is the main content of the cooling water treatment technology.
Chemicals such as corrosion inhibitors, scale inhibitors, dispersants, and biocides used in cooling water treatment can be collectively referred to as water stabilizers. The research and development and production of these chemicals are the basis of circulating water treatment. Without advanced water quality stabilizers with excellent performance and moderate price, it is impossible to talk about modern circulating water treatment. Therefore, the research and production of these water stabilizers has always been a hot spot in the water treatment industry.
2 Development of China's cooling water treatment technology and water quality stabilizer
The development of China's cooling water treatment technology was developed with the introduction of large-scale chemical fertilizers, petroleum, chemical and metallurgical devices. It started late, 30 to 40 years later than developed countries, but adhered to its own development path and aimed at foreign development. Trends, combined with national conditions for research and application, so the starting point is high and the development is fast. So far, China has developed successfully: 1 traditional phosphate formula; 2 phosphorus compound formula; 3 phosphorus alkaline water treatment formula; 4 full organic formula ; 5 molybdate water treatment formula; 6 silicate water treatment formula. Phosphorus alkaline water treatment formula and all organic formula are the main body of current domestic processing technology. These water treatment technologies reach a high level in practical industrial applications. The two main technical indicators of corrosion rate and dirt thermal resistance of the equipment can reach the international advanced level, and water treatment technology and localization of chemicals have been realized in many large-scale introduction devices. 
The development of water quality stabilizers has evolved with the development of modern cooling water treatment technologies. The development process is generally based on the development of the foundation in the 1970s, the development in the 1980s, and the development in the 1990s. At present, there are no less than 200 water quality stabilizer manufacturers in China, and the main technology relies on Tianjin Chemical Industry Research Institute and Nanjing University of Chemical Technology. However, there are only a few manufacturers with a certain scale and their own development strength. Technically speaking, the production technology of a few products has been at the international advanced level or international advanced level; some products are in the international level in the 1980s; a considerable part of the products, especially the production technology of bulk products, are still at the level of foreign countries in the 60s and 70s. 
The scale and corrosion inhibitor for circulating cooling water treatment generally consists of a dispersant, an organic phosphine, a corrosion inhibitor and the like. The following is a brief description of the development and trends of several monomers.
2.1 Dispersant
The choice and proportion of dispersant in the scale inhibitor solution have a crucial impact on the scale inhibition and the compatibility and synergy between the components.
2.1.1 Start stage
In the 1960s, the scale inhibitors and dispersants used mainly were sodium lignosulfonate, etc., which had certain scale inhibition effects, which could partially solve the problem of scale deposition and zinc salt stability, but could not meet the manufacturer's requirements for scale inhibition performance.
2.1.2 Polycarboxylate use stage
In the 1970s, polyacrylic polymers were used, and organic phosphines with excellent corrosion inhibition properties such as HEDP, ATMP, etc. were used in combination. In the late 1970s, polycarboxylic acid complex scale inhibitors and dispersants began to appear in large numbers, which made the scale inhibitor and dispersant a new step. Figures 1 and 2 show the results of some copolymers blocking CaCO 3 and Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 , showing excellent scale inhibition and dispersion properties of such copolymers.
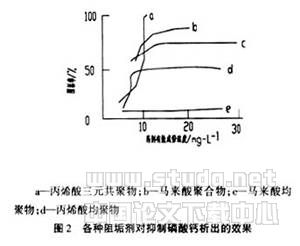
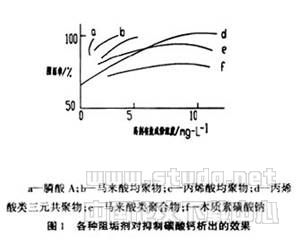
2.1.3 Polyfunctional copolymer use stage
In the 1980s, with the limitation of environmental protection on sewage discharge and the increase of circulating water concentration multiple, various high-performance copolymer scale inhibitors and dispersants appeared frequently, especially copolymers containing sulfonic acid, phosphonic acid and other functional groups, due to their properties. Excellence has caused widespread concern and application. Calg on, Nalco, Betz, Rohm & Hass in the United States, Kurita in Japan, Hass Geffers Colgue in Germany, etc., based on the development of organic sulfonic acid, unsaturated carboxylic acid binary copolymer, sulfonic acid, carboxylic acid and phosphine The development of ternary or multicomponent copolymers of acid-based functional groups is much more efficient than binary copolymers. At present, there are also manufacturers in the country to develop ternary and quaternary copolymers, the application shows that it can completely replace T-225 and other products. 
2.2 Corrosion and scale inhibitor
2.2.1 Organic phosphonates
Organic phosphonates have been rapidly developed in the 1970s due to their structurally stable phosphate content, which reduced the risk of calcium phosphate scale formation and reduced the pressure of environmental eutrophication. At present, most scale inhibitors contain organic phosphonic acids such as HEDPATMP. 
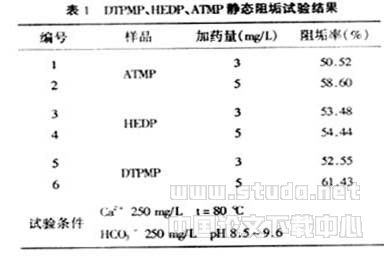
Professor Shen Hongli of Nanjing University of Science and Technology developed diethylenetriamine pentamethylphosphoric acid (DTPMP) in 1999. The test showed that the tolerance of DTPMP to calcium was greatly improved. The application in several plants showed that it can completely replace HEDP. , ATMP, EDTMP and other common organic phosphonic acid, its application can solve the problem of scale inhibition of circulating water cooling water treatment with high concentration ratio, and has a good application prospect.
2.2.2 Low Phosphorus Use Stage
In the 1980s, due to environmental protection requirements to limit phosphorus emissions, attention began to pay attention to the development of low-phosphorus, non-heavy metal corrosion inhibitors. On the one hand, the development and application of scale inhibitors with lower phosphorus content, such as 2-phosphonic butane-1, 2.4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTCA) and carboxyphosphinoacetic acid (HPAA), PBTCA phosphorus The amount is only 38.2% of HEDP. On the other hand, the compounding of organic phosphonates with other non-phosphorus agents has also been newly developed, resulting in a significant reduction in the phosphorus content of the formulation. Such as molybdenum, silicon, tungsten water treatment formulations.
2.3 Biocides
2.3.1 Oxidizing biocide
This is the first class of biocides used, the most widely used chlorine and hypochlorite, which have excellent killing and inhibition effects on microorganisms in water. But their biocidal effect of the pH of water by greater impact, the higher the pH, the worse the effect of killing, while ClO - the reaction will Nickel and copper tube B30, B30 so brass corrosion, so the high concentration rate of circulating water At high pH, ​​Cl 2 and hypochlorite are generally not used. Instead of chlorine dioxide, ClO 2 not only has a suitable pH range, but also has the ability to inhibit microorganisms better than Cl 2 and also has release properties. In recent years, ClO 2 has been used more and more in the treatment of circulating cooling water, and its production and application technology has developed rapidly.
2.2.3 Non-oxidizing biocide
Oxidative biocides and non-oxidizing biocides must be used interchangeably in circulating cooling water treatment to prevent microbial resistance to them in circulating water. The non-oxidizing biocide used mainly includes a quaternary ammonium salt, an isothiazolinone, glutaraldehyde and the like. The quaternary ammonium salt is easy to form a pseudo water level due to the use of foam during use, and has poor compatibility with the scale inhibitor. Recently, it has not been used alone in the power system. In high concentration rate circulating cooling water, glutaraldehyde composite biocide and isothiazolinone have good cost performance. It has been confirmed in many plant applications.
3 Method for increasing the concentration ratio of circulating cooling water
The supplementary water quality of circulating water in thermal power plants in Sichuan Province is relatively close, and its water quality is roughly:
Ca 2+ : 2.0 to 4.0 alkalinity: 2.0 to 4.0 mmlo / L
Cl - :<50 mg /LSO 4 2- <100 mg /L
pH: 7.0 to 8.0
Tests show that if the pH is adjusted without acid, only the scale inhibitor and biocide are added for stable water treatment. The limit concentration ratio is generally not more than 3.8, and the economic concentration ratio is generally 2.5 to 3.4. If the concentration ratio needs to be increased, To achieve the purpose of water saving, while ensuring good scale inhibition, corrosion inhibition and killing performance of the circulating water system, it can be selected from the following aspects.
3.1 Acid treatment
The circulating water is added with sulfuric acid to reduce the alkalinity, and the scale inhibitor is added to carry out the scale inhibition and corrosion inhibition treatment of the circulating cooling water, which is a relatively mature method for high concentration rate circulating water treatment. However, although many factories have acid-adding equipment, they are not used much. The reason is that the concentration ratio of operation is not high. Only the scale inhibitor can be added to achieve good scale inhibition and corrosion inhibition. Because concentrated sulfuric acid is highly corrosive, improper operation may cause burns; it is corrosive to the acid-added pipeline, and it is easy to cause corrosion and perforation of the pipeline.
However, if the concentration ratio of several open circulating water systems in Sichuan is greater than 3.5, it is necessary to add sulfuric acid for auxiliary treatment. Otherwise, the economics and reliability of the operation of increasing the concentration ratio will be difficult to guarantee.
3.2 Low Phosphorus Scale and Corrosion Inhibitor Formula
In the screening of scale inhibitors, the compatibility, compatibility and compatibilization properties of the components must be considered. At the same time, under the condition of high concentration rate operation, the low phosphorus formula should also be used. The low-phosphorus formula requires that the scale inhibitor can be developed with low phosphorus content, and on the other hand, the low phosphorus content in the circulating water is required to make it discharge sewage. Meet environmental requirements. From the current domestic water stabilizer monomers, ternary, quaternary copolymers, PBTCA, HPAA, DTPMP containing AMPS groups should be used in the formulation. T-225, polyacrylic acid, HEDP, ATMP, EDTMP, etc. should be replaced.
3.3 Supplementary water softening treatment
It is beneficial to soften part or all of the supplementary water to reduce the concentration of circulating water ions (Ca 2+ ), which is beneficial to increase the concentration ratio of circulating cooling water. From a practical point of view, it is feasible to partially replenish water for softening treatment. On the one hand, the investment in softening equipment and operating costs can be reduced. On the other hand, it is beneficial to the anti-corrosion of circulating water. The proportion of specific treatment needs to be determined through experiments.
3.4 Circulating water bypass treatment
There are two methods for sidestream treatment of some circulating water: one is to soften part of the circulating water. The second is to automatically filter some of the circulating water. The second method has been used in power plants operating at high concentration rates. In particular, the emergence of automatic backwashing filtration in recent years has led to its rapid application. 
4 circulating water monitoring technology
4.1 Automatic dosing of circulating water
High concentration ratio circulating water is essential for ensuring normal and stable dosing of circulating water due to its small cushioning property. There are two main principles for automatic dosing of circulating water: one is the automatic monitoring dosing system using fluorescence system technology. The second is an automatic dosing system that uses the change of circulating water conductance to control the concentration of the drug in the water. The target management of the concentration of the drug in the circulating water system can be controlled by the automatic dosing system to a small extent, thereby achieving a balanced operation, maximizing the effect of the agent and saving the drug.
4.2 Condenser corrosion and detection
The on-site inspection of the circulating water system is mainly through the installation of bypass coupons, small heat exchangers, corrosion and detectors, etc., directly observing the corrosion and cooling water system and the formation of biological slime, thus judging the adopted Is the circulating water treatment plan correct?
The CDH circulating water online detector developed by the Chemical Laboratory of Hebei Electric Power Research Institute has been successfully applied in the 330 M unit of Jiangyou Power Plant. It can directly observe the , corrosion and slime growth of the cooling water system. At the same time, it can quantitatively reflect the heat exchange of the copper tube of the condenser by continuously measuring the thermal resistance of the dirt, ensuring the effective treatment of the circulating water system and ensuring the safety of the unit. Stable and economic operation is of great significance.
4.3 Determination of concentration ratio
Recirculating water concentration rate is typically calculated by the formula: K = [Cl -] liable / [Cl -] Complement 
In actual operation, it was found that the chlorine ions in the circulating water increased due to the addition of chlorine-based biocide and scale inhibitor, and the water supplemented to make the chloride ions unstable, resulting in inaccurate measurement of circulating water concentration. In order to avoid these uncertainties, many petroleum and chemical plants use potassium ions to determine the concentration ratio. However, potassium ion analyzers are expensive and power plants are generally not configured. Through experiments in recent years, it has been shown that the circulating cooling water concentration ratio of thermal power plants is feasible when measuring chlorine ions in circulating water without adding chlorine-based biocides: if a chlorine-based biocide is added, the salt content is determined. Or conductivity is feasible.
Veterinary Medicine,Diarrhea Intestinal Disease,Livestock Anticoccidial Medicine,Kill Coccidia Injection Medicine
Shangqiu Meilan Biological Engineering Co.,Ltd , https://www.melanvaccine.com