Eggplant wilting may be caused by diseases such as epidemic disease, sclerotinia, stem rot, bacterial wilt, verticillium wilt, root knot nematode disease, and fertilizer damage. The specific diagnosis is as follows:
1, see the distribution of the field. When the damage occurs, the wilting occurs at noon on sunny days and returns to normal in the early evening. Severe deaths may occur. For the above other diseases, the distribution pattern of the fields is patch distribution.
2. See if there is a root knot in the root. Root knot nematode disease occurs, root knots of varying sizes can be seen at the root. The above other diseases have no root knots.
3, see if the vascular bundle becomes brown. The vascular bundles of Verticillium dahliae and bacterial wilt become brown, and these other diseases have no such symptoms. These two diseases do not show symptoms at the seedling stage and begin to show after flowering. However, Verticillium wilt from bottom to top, the vascular bundle of the stem stem is yellow-brown, and when wet, the stem base produces white mold, irregular yellowish patches appear between the leaf margin and veins, and remain near the main vein. Green, palmate mottled brown, after the site of disease withered, flower-like skin, and sometimes there will be "half crazy" phenomenon. Bacterial bacterial wilt disease, the middle and lower parts of the stem, is rough, and often grows with varying lengths of verrucose projections and adventitious roots, sometimes with brownish irregular patches on diseased stems. Such as the disease stem to do cross-section inspection, slightly squeezed, milky white mucus overflow (bacterial pus).
4, see if the roots are rotten. In the root or rhizome of eggplant root rot, the epidermis is rotted brown and easily peeled off, causing the xylem to be exposed. The above other diseases have no such symptoms.
5. See if the stem base and bifurcation are rotted. Stem rot only harms the base of stems, most of them produce water-stained dark spots 3-5 cm above and below the surface of the earth, and quickly spread to the surrounding, hand-spinning soft, yellow leaves from the bottom to the top, wilt after. One week after the diseased spot passed around the stem, the plant quickly died of blue and dry, and the underground part showed more normal. Sclerotinia mostly infects the fork at the stem part, grayish white, slightly depressed, phloem rot, and its mycelium can invade the disease stem, the later epidermis longitudinal crack, lesion size, shape, length, edge water stains, On the surface and diseased stems, white cotton flocculent hyphae and black sclerotia are present. The diseased part is wilted and dead. On the upper part of the plant, symptoms of "bending" can be formed. The epidemic disease mostly developed from stem bases and branching sites. It began to be water-stained and soon surrounded the shoots and stem bases and turned brown or dark brown spots. It spreads up and down, and the edges are not obvious, and are slightly sunken.
Bacterial bacterial wilt: At the beginning of the disease, 72% of agricultural streptomycin was used to irrigate the roots at the beginning of the disease, and another 400 times of the enemy was used for spraying.
Verticillium wilt: after colonization, the seedlings were irrigated with 70% red wettable powder 400 liquid, 0.3 kg per strain, once every 7-10 days, and 2-3 times per irrigation. In the early stage of disease, use 70% red WP to disinfect the soil or irrigate the roots. Use 1000 ml per plant, once every 10 days, 2-3 times with irrigation.
Blight: At the beginning of the disease, spray 70% red day wettable powder (thiophanate-methyl) 800 times, and 50% dry suspension 500 times. Spray once every 7 days and spray 2-4 times.
Stem rot: spraying 20% ​​chlorhexidine-phosphate 1200 times at the onset of the disease, spraying the plant stem base. Can also be applied to the Ministry of the Ministry of five chlorine nitrobenzene powder 200 times plus 50% of the United States WP 200 times, the effect is good.
Root knot nematode disease: 15 days before sowing or planting, select 10% grams of phosphor, 50% Yishuning, 3% Milur and other granules, mix well, spread and plow till the soil is spread, use per acre Quantity 3-5 kg. After planting, localized damage to the plants in the shed, available 50% phoxim EC 1500 times, or 80% dichlorvos EC 1000 times, each strain 0.25-0.5 kg to kill the root-knot nematode in the soil.
Fertilizer harm: When the fertilizer damage occurs, it is necessary to timely irrigation, spraying spray of 0.01% Tianfengsu EC 3000-4000 times, which can effectively alleviate the damage.
Sclerotinia: In the early stage of disease, 70% of the red day WP 800 times foliar spray is used for prevention and treatment. Once a week, it can be sprayed 3 times.
The cross arm and control cabinet of the Tower Crane adopt the imported high-strength aluminum alloy ofpatent technology for the one off extrusion molding, Icu Bridge and the surface undergoes the primary oxidationtreatment.
Pneumatic brake plus mechanical friction damping brake
The imported electrical machine is adopted, and the electric perpendicular moving up and down.The gas pipeline, power supply and computer communication line are separately arranged withoutinterference.The imported (GENTEC) brand German standard gas terminal (over 20,000 of inserting and pulling out) is adopted.The ICU Bridge with high bearing capacity with suspension the cavity mirror car system.The horizontal rotation function can accurately position without excursion.
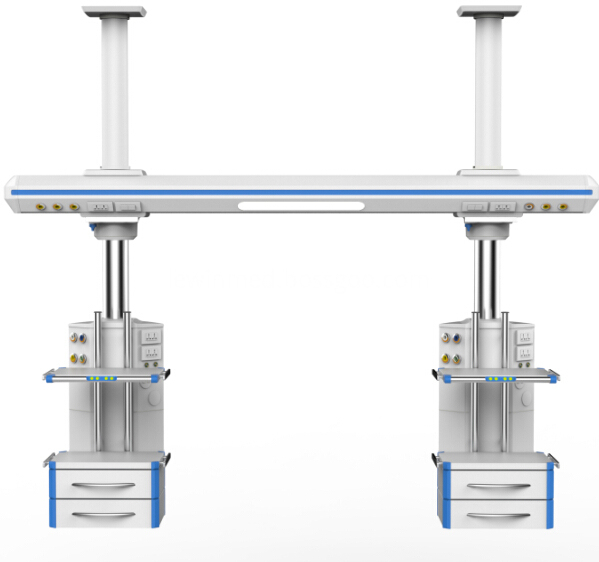
ICU Bridge
Icu Bridge,Icu Bridge Pendant,Portable Supply Unit,Tower Crane
Shandong Lewin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.lewinmed.com