1. Leaf spot disease, also known as frog eye disease, mainly damages leaves, petioles, stems, stems, and seeds. The formation of dark purple spots on the leaves, expanded to form a round or oval spots, so that the entire lesion was snake-like.
Prevention and control measures: Regular inspections, after the discovery of leaf spot disease, immediately remove diseased leaves and old leaves, bring them out of the shed to burn, and prevent repeated infections in the greenhouse. At the beginning of the disease, spray 70% chlorothalonil wettable powder 500-700 times, spray 10 times in 10 days, or use 70% mancozeb WP per acre to spray 200 kg water to 75 kg every 7-10 days Spray 1, spray 2-3 times.
2. Bud blight is also known as blight. The young shoots of the diseased plants are blue and dry, and the leaves and bracts form brown spots that gradually wither. The petiole and pedicel base become dark brown and the leaves lose their vitality and wilts droop. In the acute onset, the strawberry plants will trip, and will spread quickly without prevention and control, resulting in great losses.
Prevention and control measures: First, try to avoid seedling transplanting in the place where blight occurs. If you want to plant must use solar energy soil disinfection method to completely eliminate the fungal disease source. The second is to pay attention to appropriate sparse planting, reasonable irrigation, reduce the humidity inside the greenhouse. The third is to pay attention to timely ventilation within the shed, especially in the timely ventilation after irrigation to reduce the humidity within the shed. The fourth is to remove diseased plants in time, and it is strictly forbidden to use the diseased strain as a parent strain to cultivate strawberry seedlings, making them a source of infectious bacteria. Fifth, do a good job of chemical control. In the early stage of bud blight, 10% of polymycin 600-800 times, or 10% of Legong 300 times, or 600 grams of enemy bacteria Dan Irrigation can be used, combined with spray, spray 7 days, a total of Spray 2-3 times. In the greenhouse, 5% chlorothalonil dust agent 150-180 g/mu can be used in the greenhouse, 5-6 points can be placed, and it can be lighted and closed overnight, 7 days smoked once, smoked 2-3 times, and the effect is good.
3. Botrytis cinerea is the main disease after flowering in greenhouses. It can be affected by flowers, petals, fruits and leaves. It is mainly caused by fruit disease. It produces brown spots on enlarged fruit and gradually enlarges. Fruit softens and grows gray mold. When occurring on the leaves, brownish or dark water-stained lesions can be seen, sometimes the lesions are slightly rimmed, and on the backside of the leaves a milky white villous mycelium cluster appears under moist conditions. When infected buds and pedicels, the diseased part becomes brown. Botrytis cinerea can form a flat, or irregularly shaped, black mouse fecal sclerotium on the plant.
Prevention and control measures: First, increase organic fertilizer, reduce the amount of chemical fertilizers applied, the planting density is reasonable, the humidity in the greenhouse is controlled, and diseased plants are found in the shed. Temperature increase measures should be taken in time. The temperature in the greenhouse should be increased to 35°C every morning. Do not change the air, prevent the spread of gray mold. In case of continuous rainy weather, the disease will often recover quickly. The temperature of the shed should be raised to about 45°C for 2 hours. After this treatment, the disease can be quickly controlled. The second is to timely remove old leaves, diseased leaves and leaves and diseased inflorescences, remove diseased fruits, and concentrate deeply or burn them to eliminate the source of infection. The third is to do a good job of chemical control. Before flowering, spray with 1:1:200 Bordeaux mixture, and use 30% Shijiale 1000 times, or 50% Nongli Ling 750 times, or 10% Shi Gao 1500 times, or 50% Propionine 800-1000 times Liquid, or 50% Ketandan WP 800 times solution.
4. The anthracnose plants can have diseased leaves, petioles and stolons. The lesions on the leaves are round and irregular, the center is tan and the edges are purple. On the early stages of petioles and stolons, slightly depressed, small, central, tan-colored, purple-purple, spindle-shaped lesions spread to all petioles and entire stolons. Damage to stolons has a great impact on the strawberry seedlings. The death of the stolons will seriously affect the survival of the plants.
Prevention and control measures: Use disease-resistant varieties, use disease-free seedlings, shading and cooling, shade with shade nets, etc., to reduce the temperature of the seedbed as much as possible, thereby reducing the incidence of disease. When there is a sporadic occurrence of disease, it can be used to prevent or treat 2-3 times with 100 times liquid of carbon net rubber suspension, or 25% carbonate 500 times. The effective agents that can also be used are: Kebo 78% Borde Manganese Zinc WP 500 times, or Selemax 50% Prochloraz Manganate WP 1000x, or Easy to protect 68.75% oxone MnZnS Dispersed granules 1000 times liquid, etc., according to the development of the disease every 7 days spray 1, continuous control 3-4 times, pay attention to alternate medication, to prevent drug resistance.
5. Powdery mildew Strawberry powdery mildew occurs easily under low temperature and high humidity conditions. The suitable temperature is 15-20°C, and the relative humidity is above 90%. The environment in the winter greenhouse is exactly in line with the requirements of powdery mildew, with high frequency, strong fulminantness, and heavy damage. Strawberry leaves, stems, flowers, fruits can produce powdery mildew, diseased leaves have white powder on the lesions, the latter leaf margin atrophy, dry coke; fruit victim, the young fruit development and dry, large fruit disease on the fruit surface White powder often forms and loses its value. Severe disease may lead to the death of a large number of whole strawberry plants in the shed, or even no harvest.
Control measures: First, select disease-resistant varieties. The second is to cultivate disease-free and strong seedlings. The disease-free parent plant nursery was selected, and the weak seedlings and diseased seedlings were removed in a timely manner during the seedling raising period, and the medicine was prevented 2-3 times. The third is to do a good job of chemical control. Approximately 0.3 degree lime sulfur was sprayed on the center of the affected area and around it. After the strawberry was harvested, the whole garden was sprayed with 70% thiophanate-methyl 1000-fold solution, or 50% of the bacteriostatic 800-fold solution and 30% of Tefucon 5000-fold solution. In addition, during the initial and prosperous period of strawberry disease, the use of 24-60 grams per acre, spray 50 kilograms of water, control effect is good, and the effective period of up to 18 days, even spray 2 times can effectively control powdery mildew .
6. Verticillium wilt The disease is a soil disease. The main symptoms are the deformity of young leaves, the yellowing of leaves, and the rough surface of the leaves. Then the leaf margins turn brown and the leaves wither until they die.
Prevention and control measures: the introduction of disease-free planting; shorten the update period; disinfection and sterilization of the soil before sowing or planting, the method is to use chloropicrin 13.5-20 liters per acre, hole application or ditch application, after the application of soil cover film. Solar disinfection can also be used. The method is to deepen, irrigate, cover the mulch in the high temperature period of July-August and use the high temperature under the membrane to kill the bacteria. Before planting, dip the roots with 20% thiophanate-methyl 300-500 times for 5 minutes to prevent the seedlings from colonizing. The onset must be unplugged and burned.
7. Ascarid worms draw juice from the fruit to impede the growth of the fruit. The worm's discharge causes the leaves and fruit to be contaminated. In addition, locusts are also vectors for transmitting viruses.
Prevention measures: timely removal of old leaves, clean up the fields, eliminate weeds. Before flowering, spray 50% for 2000 times, spray 1-2 times.
8. The red spider's leaves suffered from small grey spots at the beginning of the victim's damage, and then gradually expanded, so that the entire leaves were covered with white patterns, and then the leaves were yellowed and curled, and the plants dwarfed and withered, seriously affecting the growth.
Prevention and control measures: Reasonable fertilizer management to improve the resistance of plants to spider mites, selection of avermectin, Nissoline, extermination, eradication and other agents for prevention and treatment.
Color waxy corn is generally white, yellow, red, purple and black, white, yellow and purple corn is the basic color. The purple gene in a purple/white hybrid will naturally become purple if it "beats" the white gene, and vice versa, if it's a tie, what we see is a white/purple corn. Purple can turn into red corn and black corn, which is often called "red is purple, black is purple."
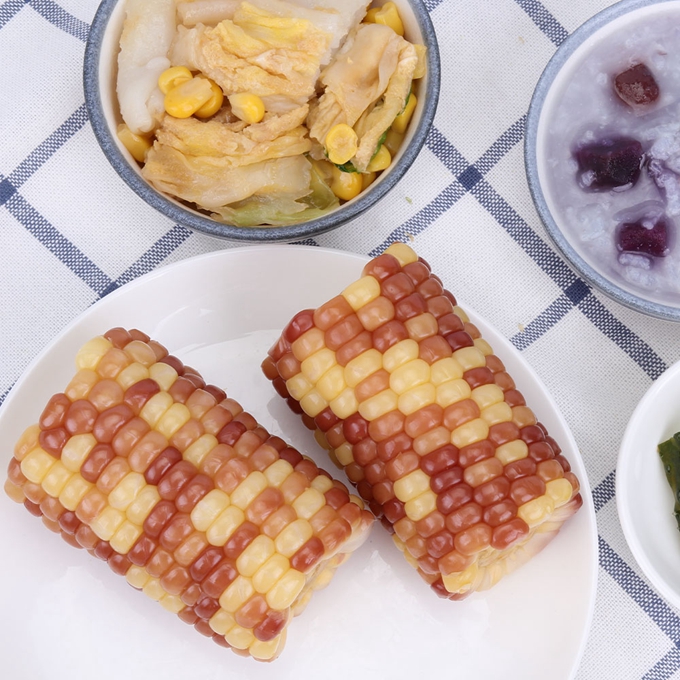
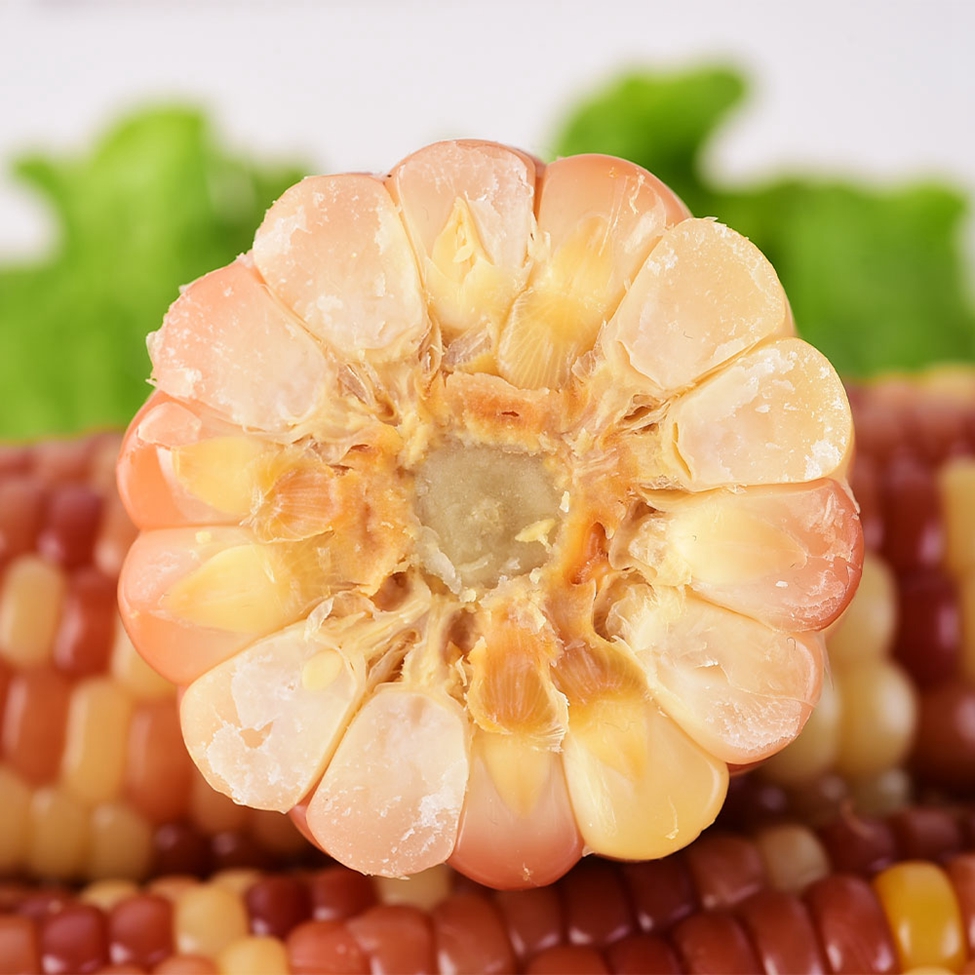
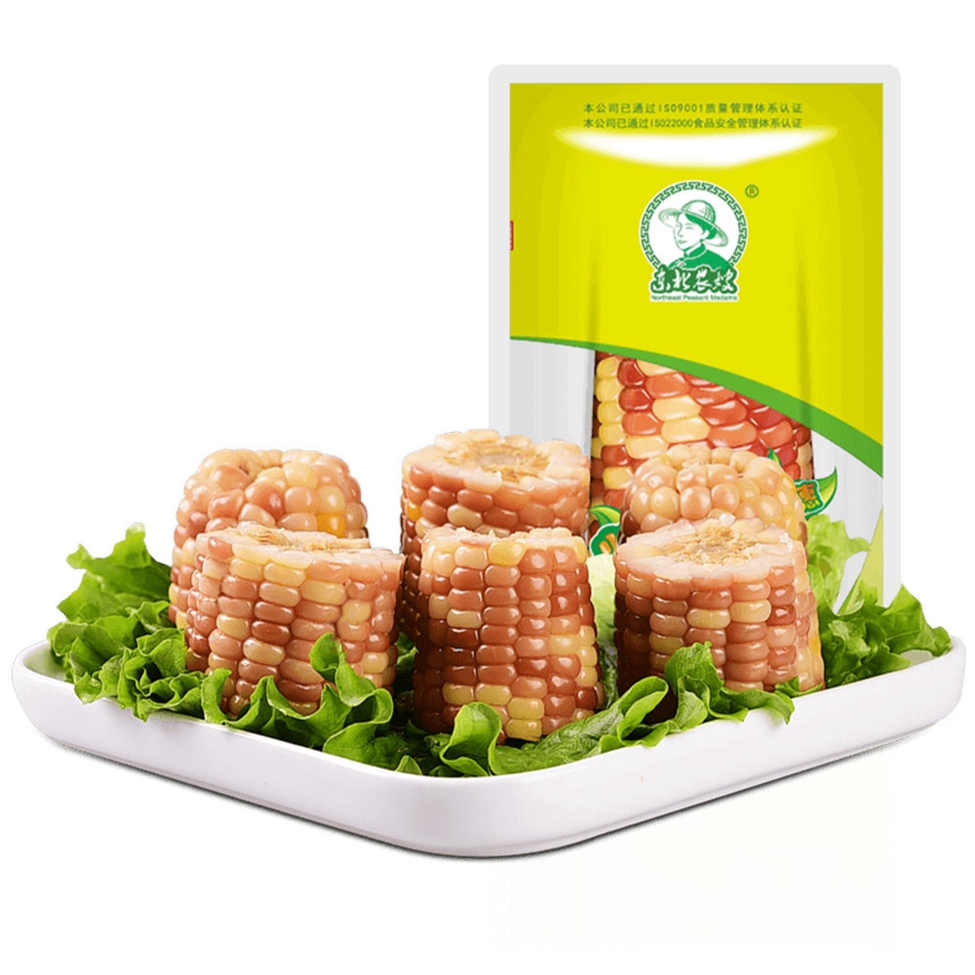



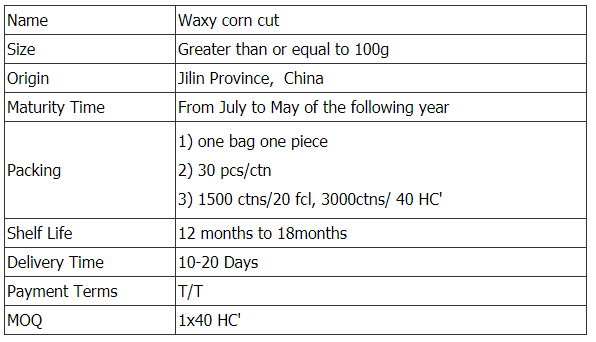
Mottled Corn Cut,Non Gmo Corn Cob,Mottled Waxy Corn Cut,Non Gmo Corn Cob Cut
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorns.com